Overview
Hybrid solar systems combine the best features of grid-tied and off-grid solar systems. They are connected to the public electricity grid but also include a battery storage system, allowing them to store excess energy. This stored energy can be used during power outages or during peak electricity demand times, providing a more flexible and reliable power solution. Hybrid systems offer energy independence while maintaining a connection to the grid, ensuring a continuous power supply and the ability to sell excess energy back to the grid.
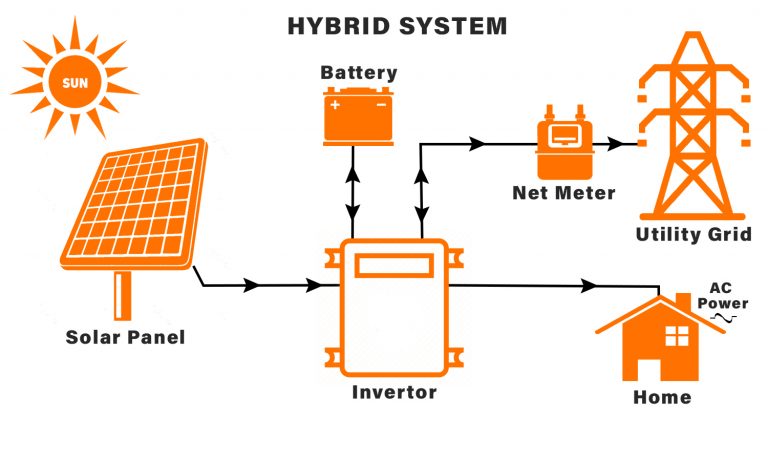
Key Components
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Inverter: Converts DC electricity from solar panels and batteries into AC electricity for household use.
- Battery Bank: Stores surplus energy for later use, providing backup power during outages or high demand.
- Charge Controller: Manages the flow of electricity between solar panels, batteries, and the grid, preventing overcharging and ensuring efficient energy use.
- Grid Connection: Allows excess energy to be exported to the grid and provides backup power when solar production and battery storage are insufficient.
- Mounting System: Securely positions solar panels to optimize sunlight capture.
- Wiring and Electrical Components: Facilitate the distribution and management of electricity within the system.
How It Works
Hybrid solar systems generate electricity from solar panels, which can be used directly or stored in a battery bank. During periods of excess production, the surplus energy is stored in the batteries. If the batteries are fully charged and there is still excess energy, it can be exported to the grid. During times when solar production is insufficient, such as at night or on cloudy days, the system can draw from the battery storage or the grid to meet energy demands. This dual approach ensures a continuous and reliable power supply.
Benefits
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on the grid by using solar energy and stored power.
- Cost Savings: Lowers electricity bills by utilizing solar energy and potentially earning from selling excess power to the grid.
- Uninterrupted Power Supply: Provides backup power during outages, ensuring continuous electricity.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces carbon footprint by relying on renewable energy sources.
Drawbacks
- Higher Initial Cost: More expensive than traditional grid-tied systems due to the inclusion of batteries and additional components.
- Complexity: Requires more sophisticated technology and maintenance compared to simpler solar systems.
- Battery Lifespan: Battery storage systems have a limited lifespan and may require replacement over time, adding to long-term costs.
Market Outlook
The market for hybrid solar systems is expanding as more consumers seek reliable and sustainable energy solutions. Advances in battery technology and decreasing costs are making these systems more accessible. Government incentives for renewable energy adoption and growing awareness of energy independence are also driving the market growth. As technology improves and economies of scale are achieved, hybrid solar systems are expected to become a more common choice for residential and commercial energy needs.




