Overview
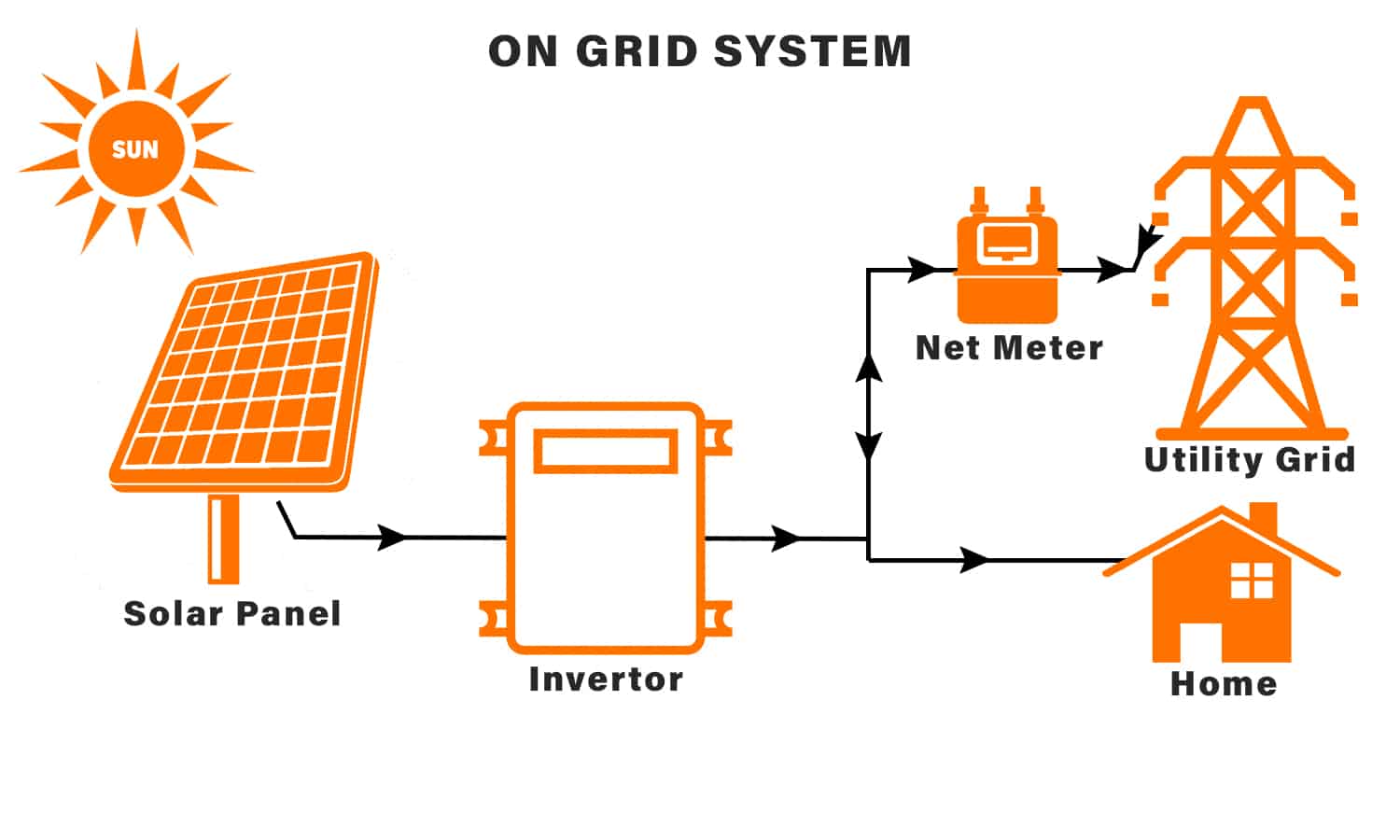
On-grid solar systems, commonly referred to as grid-tied or grid-connected systems, are the predominant type of photovoltaic (PV) setup. These systems are directly linked to the public electricity grid, allowing for seamless energy transfer between the solar panels and the grid. By eliminating the need for battery storage, on-grid systems offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for both residential and commercial applications. This integration provides a sustainable energy source without the necessity for backup power systems.
Key Components
- Solar Panels: Capture solar energy and convert it into electrical power, serving as the primary component of the system.
- Inverter: Transforms the DC electricity produced by the panels into AC electricity, suitable for use in homes and businesses as well as for feeding into the grid.
- Mounting System: Ensures the optimal positioning of panels to maximize sunlight exposure, enhancing system efficiency and longevity.
- Wiring: Connects various system components, facilitating the flow of electricity from the panels to the inverter and then to the grid.
- Net Meter: Tracks the amount of electricity exported to and imported from the grid, enabling net metering benefits such as energy credits.
How It Works
On-grid solar systems function by converting sunlight into electrical energy using solar panels. This energy is then converted from DC to AC by the inverter, making it usable for standard household or business applications. Any surplus energy generated during daylight hours can be exported to the grid, effectively reducing electricity bills through net metering. During periods without sufficient sunlight, the system draws power from the grid, ensuring a continuous supply. This dynamic interaction maximizes energy efficiency and cost savings.
Benefits
- Reduced Electricity Bills: Solar power offsets conventional electricity consumption, leading to significant savings on utility bills.
- Net Metering: Allows users to earn credits for excess electricity supplied to the grid, further enhancing financial returns.
- Simple Installation and Maintenance: The absence of batteries simplifies the installation process and reduces maintenance needs.
- Environmental Impact: Utilizes renewable solar energy, decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and reducing carbon emissions.
- Scalability: Systems can be easily expanded to accommodate growing energy needs or additional space availability.
Drawbacks
- No Backup During Outages: On-grid systems do not operate during grid outages, as they lack battery storage. This means that in the event of a power cut, the solar system will also shut down unless supplemented with an alternative backup solution such as a generator or hybrid system.
Market Outlook
The global solar energy market, including significant regions such as India, is experiencing robust growth driven by declining PV module costs and supportive government policies. India's ambitious renewable energy targets, supported by various incentive schemes, are fostering substantial investments in on-grid solar installations. This positive trajectory is expected to continue, bolstered by increasing awareness and demand for sustainable energy solutions.




